
Ever thought of numbers being presented in a way that can reveal the true data problem seamlessly? Data visualizations are just that, the magic wands for businesses that are used to make sense of the vastly diverse data pool. Data visualizations are nothing but an interestingly innovative way of presenting huge numbers or data into charts, graphs, maps, etc. You must be thinking about how can data visualization have an impact on the big number game.
Nearly all data scientists globally will likely be utilizing data visualization tools and techniques in 2025 as it is becoming increasingly essential for effectively communicating complex insights derived from data analysis. The growing deployment of data-driven decision-making across industries makes data visualization a critical skill for any data science professional thinking to barge in.
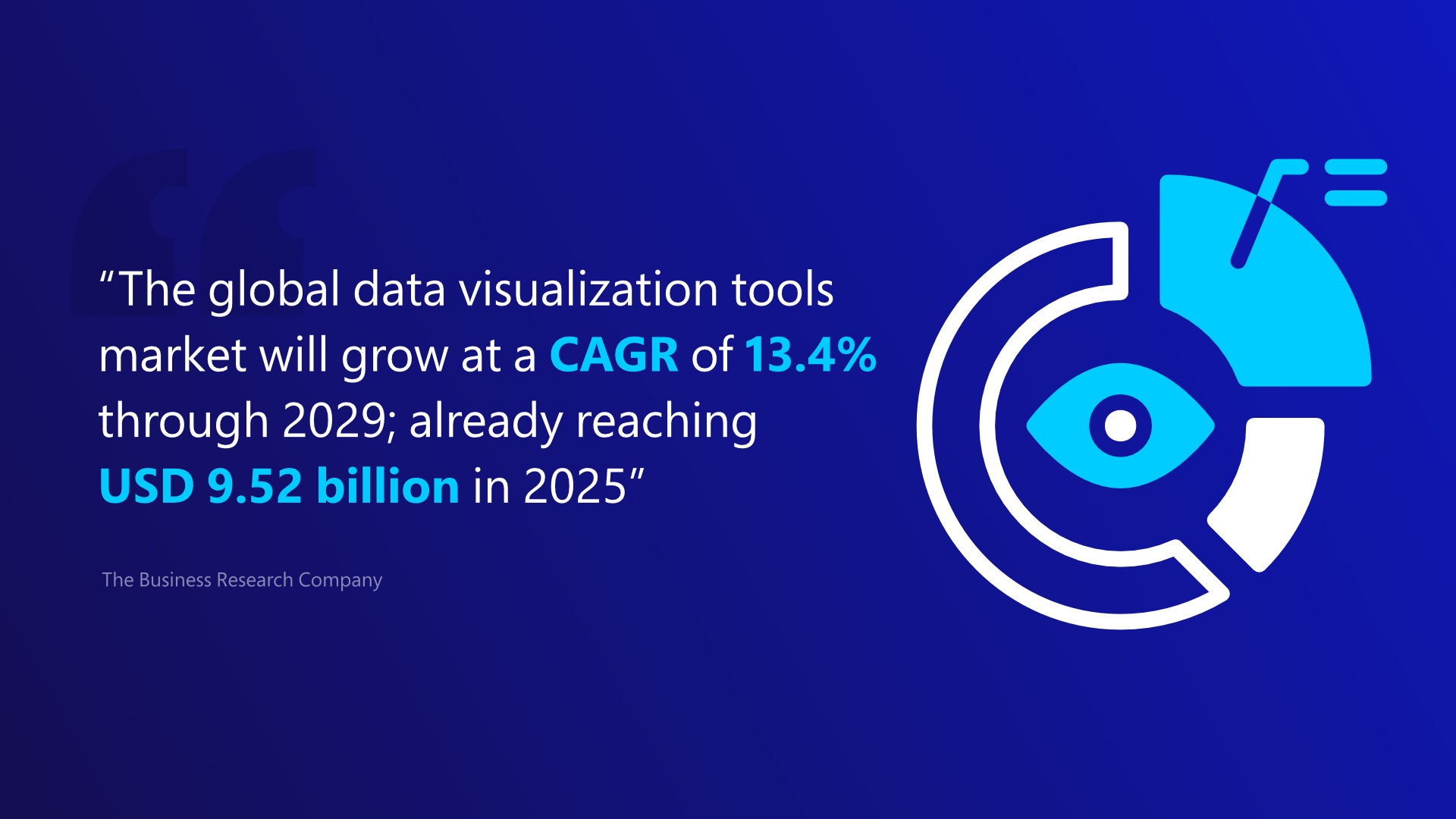
Significance of Data Visualization
In the modern business landscape, data visualization plays an essential role in helping companies recognize trends swiftly, removing the guesswork. Pictorial transformation of data makes data insights easily legible for all, empowering analysts to discover new patterns and ideas easily. Given the daily explosion of data, handling immense quantities would be nearly impossible without the help of data visualization. Now more than ever, industries across the board are banking on visualization techniques to deepen their data insights - considering the prospect of data visualization's future scope. This method allows for clearer communication of findings, ensuring companies can capitalize on the value of their data.
Understanding Data Storytelling
Gartner predicts that Data storytelling will dominate business intelligence by 2025; by becoming the most widespread means of consuming analytics. It aims to make complex information more accessible, understandable, and memorable to a wide range of audiences, including both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
Furthermore, the data science industry is expected to be heavily influenced by the widespread adoption of generative AI, with a focus on ethical practices, data privacy, and the democratization of data science tools through advancements including AutoML.
Exploring D3.js
D3.js aka Data-driven documents is a powerful JavaScript library used for creating dynamic and interactive data visualizations in web browsers. It is a free open-source JavaScript library for visualizing data and its low-level approach built on web standards offers unparalleled flexibility in authoring dynamic, data-driven graphics. D3 has powered numerous groundbreaking and award-winning visualizations, becoming a foundational building block of higher-level chart libraries.
Features of D3.js
D3’s core principle is binding data to the Document Object Model (DOM), allowing you to manipulate HTML, SVG, or Canvas elements based on your data.
D3 heavily utilizes SVG for creating visually appealing and customizable graphics that scale well across different screen sizes.
D3 provides extensive control over every aspect of your data visualization, enabling you to create unique and tailored designs.
D3 allows you to add interactivity to your visualizations, such as tooltips, zooming, panning, and animations; making them more engaging and informative.
D3 can create a variety of visualizations, including bar charts, line charts, scatter plots, pie charts, maps, network diagrams, treemaps, and more.
Steps Involved in D3.js
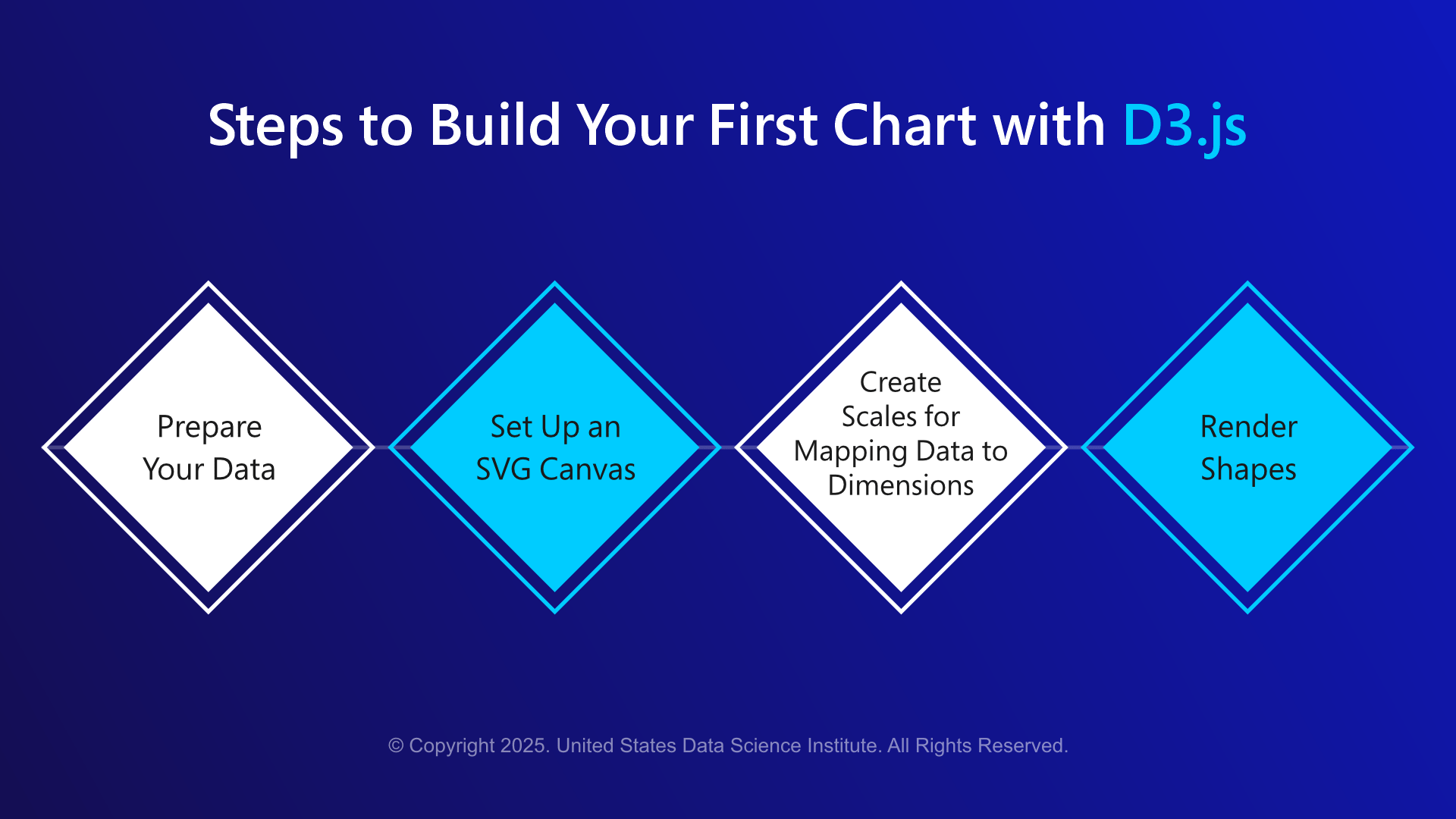
These steps in D3.js help in curating impactful data visualizations that evolve with the evolving data science industry and facilitate greater business understanding with ease.
Enhanced Visualizations with Dynamic Animations via D3.js
D3.js Potentialities Compared
|
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
|
Exploring Advanced D3.js
Advanced D3.js refers to the advanced techniques and features of the D3.js JavaScript library that can be used to create complex and dynamic data visualizations.
Tips and Tricks for Advanced D3.js
Transition chaining allows you to implement complex animation-like transitions to add a new level of interactivity to your data. It is great for showing future effects or for drawing attention to certain elements during a presentation.
Web links are best used to allow users to naturally explore the data or to give access to extra resources that may help them understand your graph.
You can add a table by itself or alongside your graph. Including a table with your graph allows your users to get a closer look at each data point and learn the exact values that make up the graph.
One easy way to do this is to allow users to hide certain data points to get a closer look at relationships or trends. The more data points you have on the same graph, the more useful this function becomes.
This is helpful when parsing large data sets for outliers or data beyond a certain threshold, such as those that take place on a particular date.
D3.js- Challenges and Solutions
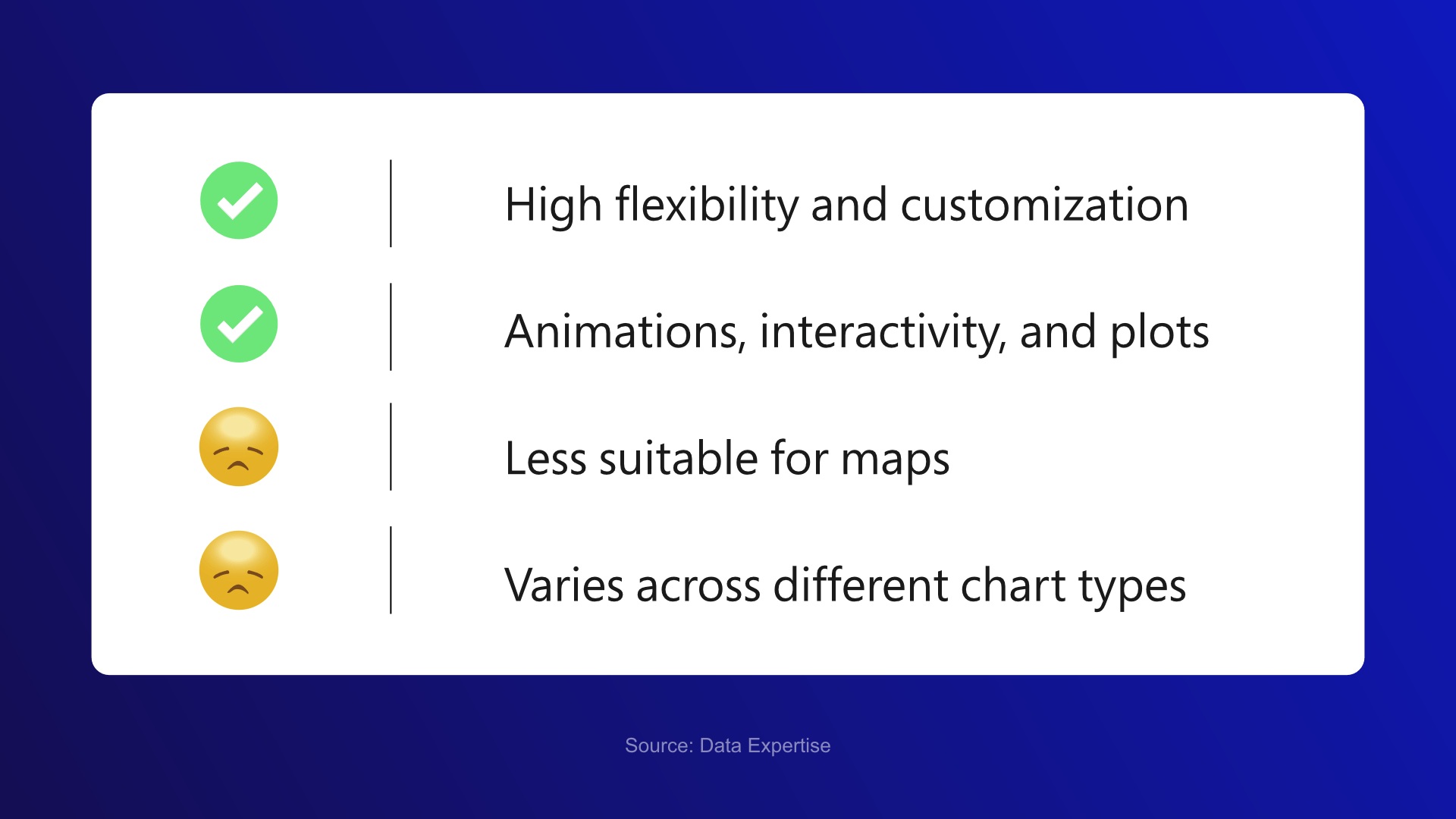
Effective D3.js visualizations also require a balance between aesthetic design and functionality, ensuring that data visualizations are not only visually appealing but also user-friendly and accessible. By addressing these challenges and adhering to best practices, developers can harness the full potential of D3.js to create visualizations that are both powerful and effective in conveying data-driven stories. Understanding behind-the-scenes of the data science industry is a must that is facilitated with D3.js and other diversely equipped data science tools; to foster long-term uninterrupted growth.
This website uses cookies to enhance website functionalities and improve your online experience. By clicking Accept or continue browsing this website, you agree to our use of cookies as outlined in our privacy policy.